This circuit was designed for use in a hifi showroom, where a choice of speakers could be connected to a stereo amplifier for comparative purposes. It could be used for other similar applications where just one of an array of devices needs to be selected at any one time. A bank
of mechanically interlocked DPDT pushbutton switches is the simplest
way to perform this kind of selection but these switches aren’t readily
available nowadays and are quite expensive. This simple circuit performs
exactly the same job. It can be configured with any number of outputs
between two and nine, simply by adding pushbutton switches and relay driver circuits to the currently unused outputs of IC2 (O5-O9).
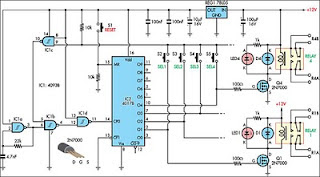
Gate IC1a is connected as a relax-ation oscillator which runs at about 20kHz. Pulses from the oscillator
are fed to IC1b, where they are gated with a control signal from IC1c.
The result is inverted by IC1d and fed into the clock input (CP0) of
IC2. Initially, we assume that the reset switch (S1) has been pressed,
which forces a logic high at the O0 output (pin 3) of IC2 and logic lows
at all other outputs (O1-O9). As the relay driver transistors
(Q1-Q4) are switched by these outputs, none of the relays will be
energised after a reset and none of the load devices (speakers, etc)
will be selected. Now consider what happens if you press one of the
selector switches (S2-S5, etc). For example, pressing S5 connects the O4
output (pin 10) of IC2 to the input (pin 9) of IC1c, pulling it low.
Circuit diagram:
Pushbutton Relay Selector Circuit Diagram
This causes the output (pin 10) to go high, which in turn pulls the
input of IC1b (pin 5) high and allows clock pulses to pass through to
decade counter IC2. The 4017B counts up until a high level appears at
its O4 output. This high signal is fed via S5 to pin 9 of NAND gate
IC1c, which causes its output (pin 10) to go low. This low signal also
appears on pin 5 of IC1b, which is then inhibited from passing further
clock pulses on its other input (pin 6) through to its output (pin 4),
thus halting the counter. So, the counter runs just long enough to make
the output connected to the switch that is pressed go high. This
sequence repeats regardless of which selector switch you press, so the
circuit functions as an electronic interlock system.
Each relay driver circuit is a 2N7000 FET switch with its gate driven
from one output of IC2 via a 100W resistor. The relay coil is connected
from the drain to the 12V supply rail, with a reverse diode spike suppressor
across each coil. If you want visual indication of the selected output,
an optional indicator LED and series resistor can be connected across
each relay coil, as shown. For
selecting pairs of stereo speakers, we’d suggest the use of relays like
the Jaycar SY-4052. These operate from 12V and have DPDT contacts rated
for 5A. Note that although four selector switches are shown in the circuit, only two relay drivers are shown because of limited space. For a 4-way selector, identical relay drivers would be driven from the O2 and O3 outputs of IC2.
Author: Jim Rowe - Copyright: Silicon Chip Electronics
No comments:
Post a Comment